Polyethylene (PE) is a widely used thermoplastic with numerous applications in everyday life and industry. It comes in various types, each with unique properties, advantages, and roles. Eco Plastic will help you understand PE more clearly and how to apply it effectively.
.jpg)
1. Overview About Polyethylene (PE)
Polyethylene (PE), with the chemical formula (C₂H₄)n, is a thermoplastic polymer synthesized through the polymerization of ethylene monomers. It is the most commonly produced plastic worldwide, known for its versatility, durability, and cost-effectiveness. PE is typically translucent or white in its natural state, but it can be manufactured in various colors, including black and white, to meet specific application needs. White PE is often used in applications requiring a clean aesthetic or where light reflection is beneficial.
2. Types of Polyethylene
PE is categorized based on its density and molecular structure, leading to different types with distinct properties and applications:
2.1 Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE)
- Density: 0.910 – 0.925 g/cm³
- Properties: Flexible, transparent, and resistant to moisture.
- Applications: Food packaging, plastic bags, and containers.
2.2 High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE)
- Density: 0.941 – 0.965 g/cm³
- Properties: Stiff, resistant to impact and chemicals.
- Applications: Milk jugs, detergent bottles, and piping.
2.3 Linear Low-Density Polyethylene (LLDPE)
- Density: 0.915 – 0.930 g/cm³
- Properties: Stretchable and resistant to impact.
- Applications: Stretch films and agricultural films.
2.4 Medium-Density Polyethylene (MDPE)
- Density: 0.926 – 0.940 g/cm³
- Properties: Moderate strength and resistance to chemicals.
- Applications: Gas pipes and fittings.
2.5 Ultra-High Molecular Weight Polyethylene (UHMWPE
- Properties: Extremely high tensile strength and abrasion resistance.
- Applications: Medical devices, bulletproof vests, and industrial liners.
2.6 Cross-Linked Polyethylene (PEX)
- Properties: Enhanced thermal and chemical resistance.
- Applications: Hot water pipes and radiant heating systems.
2.7 White Polyethylene
- Properties: Achieved by adding white masterbatch during production, resulting in a bright, opaque finish.
- Applications: Food packaging, medical containers, and products requiring a clean appearance.
Types of Polyethylene
3. Key Properties of Polyethylene
PE's versatility stems from its distinct properties:
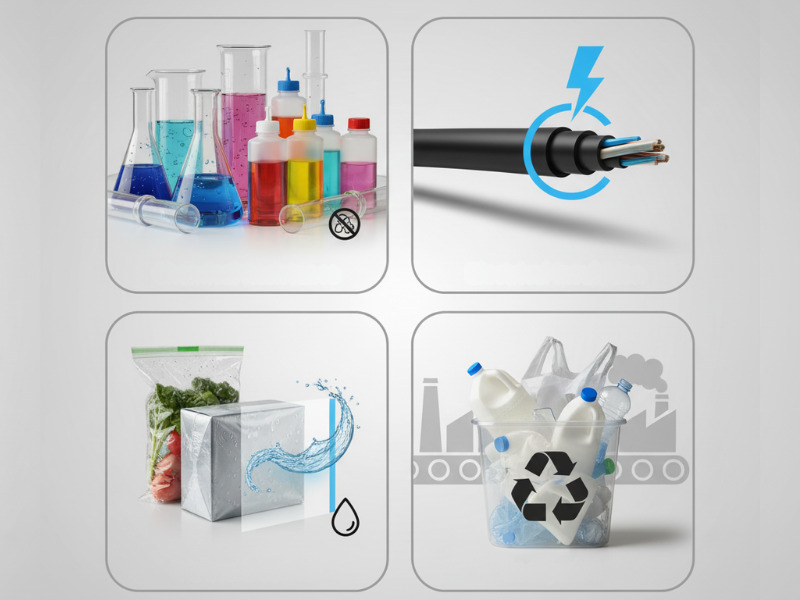
- Chemical Resistance: PE is resistant to a wide range of chemicals, making it suitable for containers and pipes.
- Electrical Insulation: Its non-conductive nature is advantageous in electrical applications.
- Moisture Barrier: PE serves as an effective barrier against moisture, preserving the integrity of contents.
- Recyclability: PE is recyclable, contributing to sustainable practices when properly processed.
Key Properties of Polyethylene
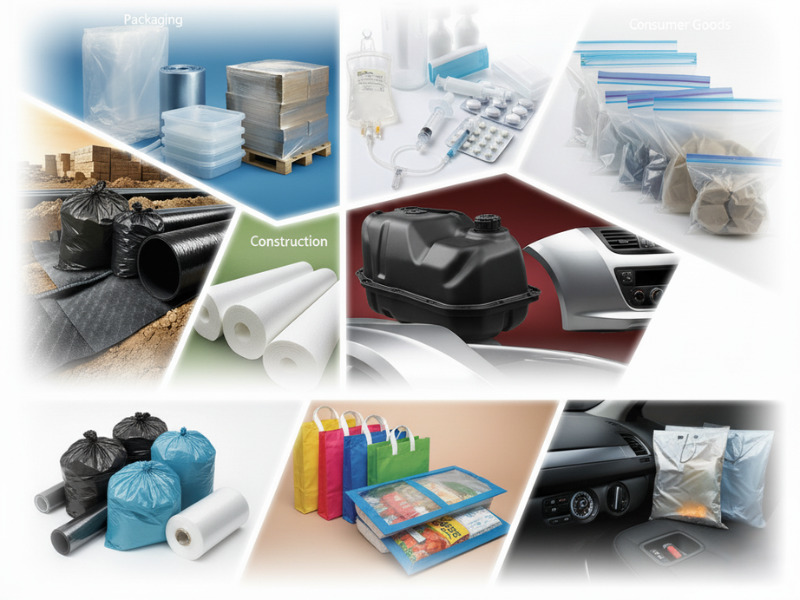
4. Applications Across Industries
PE's adaptability allows its use in various sectors:
- Packaging: LDPE and LLDPE are commonly used for making plastic bags, wraps, and containers.
- Construction: HDPE is used for piping, geomembranes, and insulation.
- Automotive: PE is utilized in fuel tanks, bumpers, and interior components.
- Healthcare: PE is used in medical devices, containers, and packaging.
- Consumer Goods: PE is found in toys, household items, and textiles.
Applications Across Industries
5. Advantages of Polyethylene
- Cost-Effective: PE's abundance and ease of production make it economically viable.
- Durability: Resistant to wear and tear, ensuring longevity of products.
- Versatility: Can be molded into diverse shapes and sizes to meet specific needs.
- Safety: Generally considered safe for food contact and medical applications.
Advantages of Polyethylene
6. Considerations and Limitations
Despite its benefits, PE presents certain challenges:
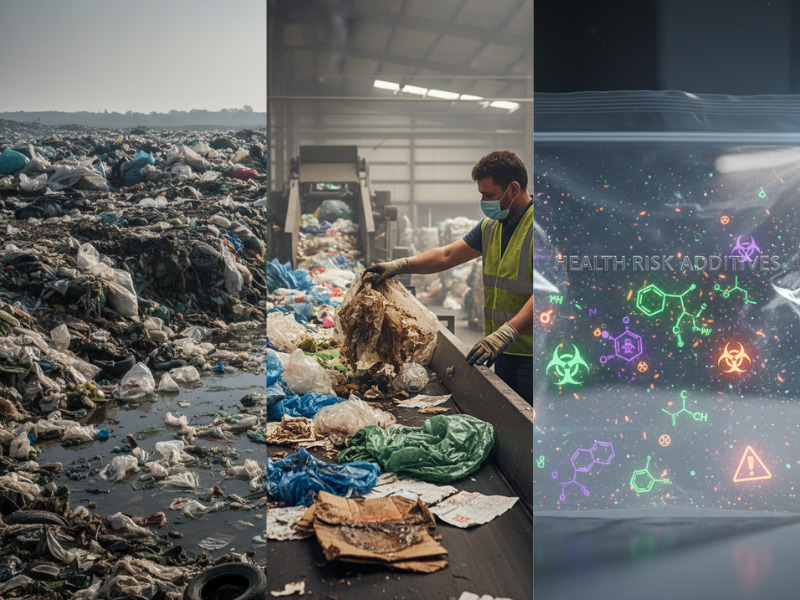
- Environmental Impact: Non-biodegradability leads to accumulation in landfills and oceans.
- Recycling Challenges: Contamination can hinder recycling processes.
- Additives: Some PE products may contain additives that raise health concerns.
Considerations and Limitations
7. Sustainable Manufacturing Practices
To mitigate environmental concerns, sustainable practices in PE production include:
- Recycling Initiatives: Encouraging the reuse of PE materials to reduce waste.
- Bio-Based PE: Developing PE from renewable resources like sugarcane.
- Energy-Efficient Production: Implementing processes that consume less energy and reduce emissions.
Sustainable Manufacturing Practices
8. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
8.1 Is PE safe for food packaging?
Yes, PE is widely used in food packaging and is generally recognized as safe when used appropriately.
8.2 Can PE be recycled?
Yes, PE is recyclable, though the process can be challenging due to contamination and sorting issues.
8.3 What is the difference between white and black polyethylene?
White PE is opaque and used for aesthetic purposes, while black PE often contains carbon black for UV resistance.
Conclusion
Polyethylene remains a cornerstone material in modern industry due to its diverse properties and applications. While it offers numerous benefits, addressing its environmental impact through sustainable practices is crucial. By understanding PE's characteristics and challenges, industries can make informed decisions that balance utility with responsibility.

.jpg)